Ordering information
Name
Cat. No.
Vol.
Scheme
G-Strep
PMG015-2
PMG015-5
2 ml
5 ml
1. Overview
PuriMag™ G-Strep Streptavidin Magnetic Beads universally bind any biotinylated molecules – such as antibodies, proteins, peptides, and DNA – through the high-affinity interaction between streptavidin and biotin. They feature a large surface area of particles and high capture efficiency.The PuriMag G-Strep streptavidin-biotin biomolecule complexes can be easily separated from unbound biotinylated biomolecules using a magnet, thus providing a rapid and streamlined method for labeling biomolecules with magnetic nanoparticles.The purified nanoparticle-biomolecule complexes are suitable for various downstream separation processes: Protein Purification, Cell Separation, Immunoprecipitation, and Molecular Detection.
Binding Capacity:
~50 μg Streptavidin/mg beads;
>4000 pmol free biotin/mg beads;
>300 pmol biotin-oligonucleotide/mg beads;
>20 pmol biotin-dsDNA fragments/mg beads;
2. product description
Product Specifications
Description
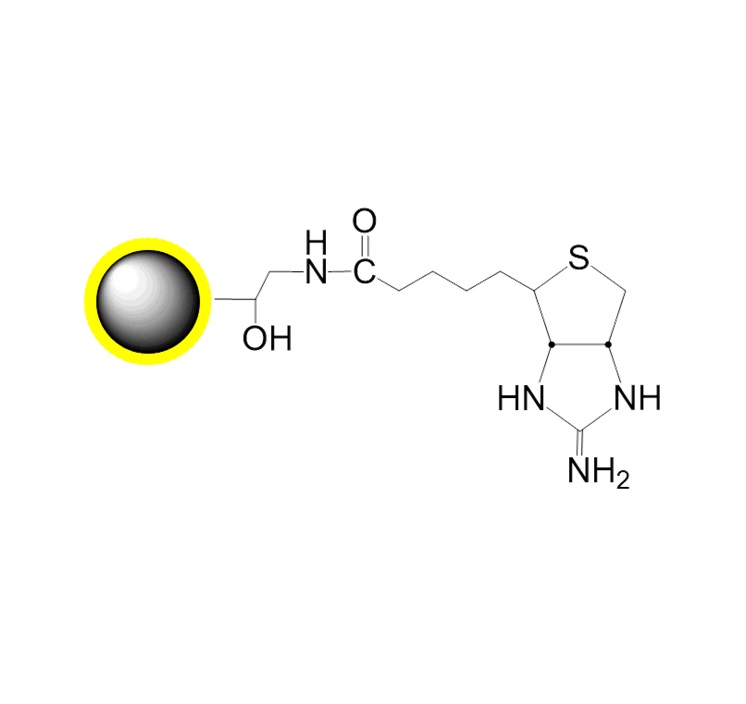
Polymer coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles
Particle Size
200 nm
Number of Beads
~1.7×1010 beads/mg
Matrix
Proprietary polymer
Functional group
Streptavidin group
Group density
~50 μg streptavidin / mg Beads
Magnetization
60~70 EMU/g
Formulation
10mg/mL in 25 mM tris-HCl, 0.15 M NaCl, 0.05% tween20, 0.09% NaN3, pH 7.2
Storage
1 year at 2~8 ℃. Do not freeze.
Binding Capacity:
Each batch of SA magnetic particles is tested for minimum guaranteed binding capacity using free biotin.
Non-specific Protein Binding:
2 mg SA magnetic particles are incubated with 0.2 mg IgG in 200 μL of 50 mM phosphate buffer (0.15 M NaCl, pH 7.2) for 1 h at 15–25°C. After washing with 2 × 200 μL incubation buffer, the protein concentration in the supernatant is measured (A280). No unspecific binding is detected.
DNase Activity:
1 μg DNA substrate is incubated for 4 h at 37°C in 100 μL Buffer M (10 mM Tris-HCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 50 mM NaCl, 1 mM dithioerythritol, pH 7.5) with 1 mg SA magnetic beads. No DNase activity is detected.
RNase Activity:
5 μg MS2 RNA are incubated for 4 h at 37°C in 100 μL 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) with 1 mg SA magnetic particles. No ribonuclease activity is detected.
Protease Activity:
10 mg SA beads are incubated with casein-resorufin in 200 μL 0.2 M Tris-HCl (20 mM CaCl2, pH 7.8) for 30 min at 37°C. After TCA precipitation, protease activity correlates with supernatant absorbance at 574 nm. No protease activity is detected.
4. Workflow Procedures
Example 1: Binding of Biotinylated Nucleic Acids to SA Magnetic Beads
This protocol is suitable for binding biotinylated oligonucleotides and dsDNA.
1.Vortex beads for 20 seconds before use.
2.Pipette the required volume of PuriMag beads into a nuclease-free microcentrifuge tube. Separate magnetic particles.
*Note: 50 μL @ 10 mg/mL (500 μg) is sufficient to bind 125 pmol (~80 μg) biotinylated oligonucleotide or biotinylated PCR product (~40 μg @ 500 bp).*
3.Discard supernatant. Resuspend beads in 100 μL Binding Buffer (20 mM Tris-Cl, 1.0 M NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 0.02% Triton® X-100; pH 7.8).
4.Incubate appropriate amount of biotinylated oligonucleotide with resuspended beads for 15 min at RT with gentle mixing.
5.Separate beads and wash twice with Binding Buffer.
6.Resuspend beads in DEPC-treated water. Oligonucleotide-coated particles are now ready for downstream applications.
Example 2: mRNA Purification from Total RNA
1.Vortex beads for 20 seconds before use.
2.Pipette required bead volume into nuclease-free tube. Magnetically separate beads.
3.Discard supernatant. Resuspend beads in 100 μL Binding Buffer (20 mM Tris-Cl, 0.5 M NaCl; pH 8.0).
4.Incubate appropriate amount of 5'-biotinylated oligo(dT) with resuspended beads from Step 3 for 15 min at RT (15–25°C).
5.Magnetically separate beads. Discard supernatant and wash oligo-bound beads twice with 200 μL Binding Buffer.
6.Add DEPC-treated water to total RNA sample to final volume of 90 μL.
7.Incubate total RNA at 55°C for 5 min to disrupt secondary structures.
8.Add 10 μL 5M NaCl to total RNA sample.
9.Add total RNA to washed beads from Step 5. Mix gently and hybridize for 3 min at RT.
10.Magnetically separate beads and discard supernatant. Wash with 150 μL Wash Buffer (7 mM Tris-Cl, 0.17 M NaCl; pH 8.0).
11.Elute mRNA with appropriate volume of DEPC water at 55°C for 2 min. Separate beads and transfer supernatant to new tube.
Example 3: Immobilization of Biotinylated Antibodies
1.Vortex beads for 20 seconds before use.
2.Add 50 μL (0.5 mg) beads to 1 mL Binding Buffer (TBS-0.05% Tween 20 detergent). Wash beads twice with Binding Buffer.
3.Resuspend particles in 450 μL Binding Buffer.
4.Add 50 μL serum or cell culture supernatant to particles.
5.Note: Adjust sample volume per user preference. If sample volume <500 μL, dilute to 500 μL final volume with Binding Buffer.
6.Mix gently on rotator for 30 min.
7.Magnetically separate beads and discard supernatant. Wash twice with 0.5 mL Binding Buffer.
Example 4: Cell Enrichment
Magnetic nanoparticles are ideal for isolating cells (e.g., CTCs, stem cells) from mixed cell populations obtained from tissues or organs.
1.Vortex beads for 20 seconds before use.
2.Aliquot sufficient PuriMag Streptavidin beads for enrichment.
3.Note: 20 μL typically enriches up to 1×10⁷ cells.
4.Wash beads twice with 500 μL Wash Buffer (TBS-0.05% Tween 20 detergent). Magnetically separate and discard supernatant.
5.Add biotinylated antibody to nanoparticles and incubate 15-30 min on sample rotator.
*Note: 20 μL nanoparticles bind 50-1000 ng antibody.*
6.Wash bead-antibody conjugates twice with 500 μL Wash Buffer.
7.Resuspend nanoparticle-antibody conjugate in Wash Buffer (20-50 μL), then add to cell sample (total volume 1-5 mL).
8.Incubate beads with cell sample on rotator for 30-60 min at RT.
9.After incubation, separate nanoparticle-bound cells from solution using magnet and carefully remove supernatant.
10.Wash beads twice with 500 μL Wash Buffer.
11.Isolated cells may be kept on ice for immediate downstream applications or suspended in culture medium for growth.
Example 5: Release of Immobilized Biotinylated Molecules
The biotin-streptavidin bond is disrupted under harsh conditions:
-
96% dissociation of immobilized biotinylated DNA is typically achieved by:
a) 5-min incubation at 65°C, or
b) 2-min incubation at 90°C in 95% formamide/10 mM EDTA (pH 8.2) -
Alternatively, boil samples in 0.1% SDS for 5 min for protein dissociation.
*Note: Proteins denature under these treatments, and streptavidin beads cannot be reused. Biotin-streptavidin interactions may also be disrupted by brief incubation in deionized water >70°C.*