Ordering information
Name
Cat. No.
Vol.
Scheme
GS-COOH
(10 C spacer)
PMG007-2
PMG007-5
2ml
5ml
GL-COOH
(20 C spacer)
PMG008-2
PMG008-5
2ml
5ml

1. Overview
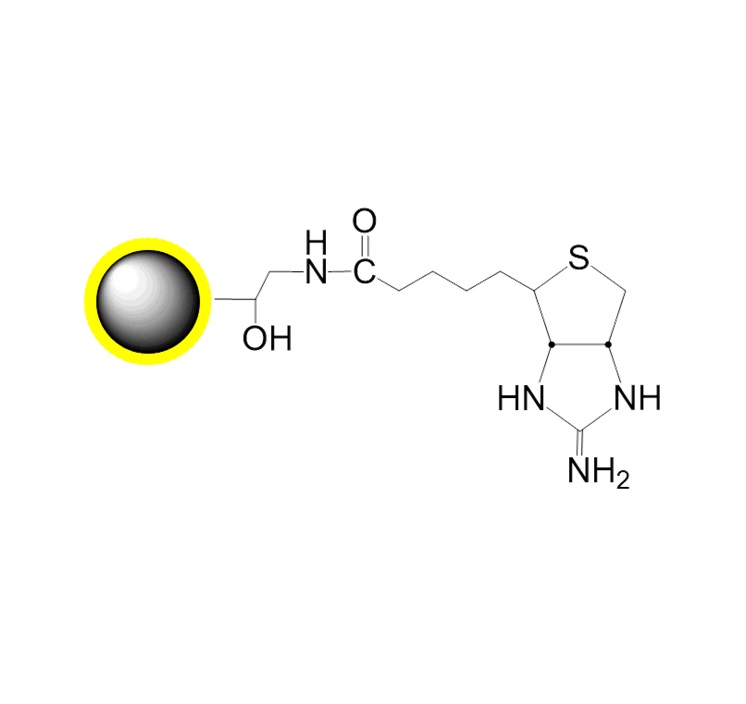
PuriMag™ G-COOH carboxyl-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles are uniform, polymer-coated superparamagnetic nanoparticles. Their hydrophilic surface ensures excellent dispersibility, low non-specific adsorption, and easy handling in various buffers. The surface is coated with a high density of carboxyl functional groups, enabling permanent immobilization of various amine-containing ligands.
The surface carboxyl groups (COOH) can be used for covalent coupling of ligands such as proteins, peptides, and nucleic acids. Activation of the magnetic beads' surface carboxyl groups with EDC allows ligands to couple via their primary amine groups, forming stable amide bonds.
PuriMag™ G-COOH magnetic beads are suitable for various magnetic separation applications, including affinity enrichment, protein purification, immunoprecipitation, and cell sorting.
2. product description
|
Product Specifications |
|
|
Description |
Polymer coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles |
|
Particle Size |
200 nm |
|
Number of Beads |
~1.7×1010 beads/mg |
|
Matrix |
Proprietary polymer |
|
Functional group |
Carboxyl group |
|
Group density |
~300 µmole / g of Beads |
|
Magnetization |
60~70 EMU/g |
|
Formulation |
10 mg/ml suspension in DI water |
|
Stability |
pH 3.5~10, 4~80 ℃, most organic solvents |
|
Storage |
1 year at 2~8 ℃. Do not freeze. |
3. Instructions for Use
Coupling Buffer: 50 mM MES [2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid], pH 6.0, 0.01% Triton X-100.
Coupling Reagents:
EDC [1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide];
Sulfo-NHS [N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide] (Optional).
Quenching Buffer: TBS (25 mM Tris-Cl, 130 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl), pH 8.0, 0.01% Triton X-100.
Storage Buffer: TBS or PBS containing 0.01% Triton X-100 or 0.01% Tween 20. Add preservative if required.
The following protocol describes ligand coupling to 100 μL of carboxyl magnetic beads. This protocol can be scaled up or down as needed. Optimization of bead activation conditions (EDC, EDC/NHS, pH) and coupling conditions (ligand concentration, coupling buffer, pH, reaction volume, and incubation time) is strongly recommended.
Notes:
■ Ensure uniform suspension of magnetic beads by vortexing.
■ For optimal performance:
Perform coupling in amine-free buffers.
Protein concentration: 0.5–4 mg/mL; oligonucleotide concentration: 20–100 μM (free of other proteins).
Higher protein concentrations allow flexible optimization of reaction volumes.
Avoid buffers containing Tris, glycine, acetate, or citrate.
■ 50 mM MES buffer (pH 6.0) with 0.01% Triton X-100 may be used for activation and coupling.
Chemically synthesized oligonucleotides must contain a 5′-amine group for bead coupling.
■ Beads contain 0.5% SDS to stabilize the suspension. Although not strictly required, including 0.01–0.05% Triton X-100 or 0.01–0.05% Tween 20 in all buffers will prevent bead aggregation and improve dispersion.
Coupling Protocol A: Two-Step Coupling Using EDC
(Recommended for coupling proteins to PuriMag™ Carboxyl Beads)
This protocol first activates the carboxyl groups on the beads using the water-soluble carbodiimide EDC to form amine-reactive intermediates. After removing EDC, the protein ligand is added and couples via its primary amines to the activated carboxyl groups on the beads.
1.Ensure the protein/ligand is in amine-free coupling buffer. Use 50–400 μg protein per 100 μL coupling buffer. Keep on ice.
2.Vortex the carboxyl beads to resuspend. Transfer 100 μL beads to a 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tube. Separate magnetically and remove supernatant.
3.Add 200 μL coupling buffer, vortex for 20 sec. Separate magnetically and remove supernatant.
4.Repeat wash (Step 3) twice more.
5.Prepare fresh EDC solution (50 mg/mL) in coupling buffer.
6.Add 80 μL coupling buffer and 20 μL fresh EDC solution to the beads. Mix well. Incubate at room temperature (RT) for 15 min. Separate magnetically and remove supernatant.
7.Wash beads with 200 μL coupling buffer, vortex to mix. Separate magnetically and remove supernatant immediately (amine-reactive intermediates are unstable).
8.Add 100 μL coupling buffer and 50–400 μg protein/ligand to the beads. Vortex to mix.
9.Incubate at RT for 30 min (optimal time may range from 0.5–4 h depending on ligand and concentration).
10.Place tube in magnetic stand, separate magnetically, and remove supernatant (Save supernatant for analysis if optimizing protocol; contains unbound ligand).
11.Add 500 μL quenching buffer to beads. Vortex for 20 sec. Separate magnetically and remove supernatant.
12.Add 500 μL quenching buffer to beads. Incubate at RT for 30–60 min. Separate magnetically and remove supernatant.
13.Add 500 μL quenching buffer to beads. Vortex vigorously for 20 sec. Separate magnetically and remove supernatant. Repeat this wash twice more.
14.Remove tube from magnetic stand. Add 100 μL storage buffer. Vortex to mix and store beads at 2–8°C.
Coupling Protocol B: Two-Step Coupling Supplemented with Sulfo-NHS
(Similar to Protocol A but uses Sulfo-NHS to stabilize intermediates and enhance efficiency)
1.Ensure protein/ligand is in amine-free coupling buffer. Use 50–400 μg protein per 100 μL coupling buffer. Keep on ice.
2.Vortex carboxyl beads to resuspend. Transfer 100 μL beads to a 1.5 mL tube. Separate magnetically and remove supernatant.
3.Add 200 μL coupling buffer, vortex vigorously for 20 sec. Separate magnetically and remove supernatant.
4.Repeat wash (Step 3) twice more.
5.Prepare fresh solutions in coupling buffer: EDC (50 mg/mL) and Sulfo-NHS (50 mg/mL).
6.Add 60 μL coupling buffer, 20 μL fresh EDC solution, and 20 μL fresh Sulfo-NHS solution to the beads.
7.Mix and incubate at RT for 15 min. Separate magnetically and remove supernatant.
8.Wash PuriMag™ beads with 200 μL coupling buffer. Vortex to mix. Separate magnetically and remove supernatant.
9.Add 100 μL coupling buffer and 50–400 μg protein/ligand. Vortex to mix. Incubate at RT for 0.5–4 h.
10.Place tube in magnetic stand, separate magnetically, and remove supernatant (Save for analysis if optimizing).
11.Add 250 μL quenching buffer to beads. Vortex for 20 sec. Separate magnetically and remove supernatant.
12.Add 500 μL quenching buffer to beads. Incubate at RT for 30–60 min. Separate magnetically and remove supernatant.
13.Add 250 μL quenching buffer to beads. Vortex vigorously for 20 sec. Separate magnetically and remove supernatant.
14.Remove tube from magnetic stand. Add 100 μL storage buffer. Vortex to mix and store beads at 2–8°C.
Coupling Protocol C: Single-Step Coupling
(Fast protocol where beads, EDC, and ligand are added simultaneously. Best for oligonucleotides/small molecules when activation doesn't interfere)
1.Ensure protein/ligand is in amine-free coupling buffer. Use 50–400 μg protein or 1–5 nmol oligonucleotide per 100 μL coupling buffer. Keep on ice.
2.Vortex carboxyl beads to resuspend. Transfer 100 μL beads to a 1.5 mL tube. Separate magnetically and remove supernatant.
3.Add 200 μL coupling buffer, vortex vigorously for 20 sec. Separate magnetically and remove supernatant.
4.Repeat wash (Step 3) twice more.
5.Remove tube from magnetic stand. Add 50–400 μg ligand in 80 μL coupling buffer to the beads.
6.Incubate at RT for 30 min.
7.Prepare fresh EDC solution (50 mg/mL) in coupling buffer.
8.Add 20 μL fresh EDC solution to the bead mixture. Vortex to mix. Incubate at RT for 0.5–4 h with continuous mixing.
9.Separate magnetically and remove supernatant (Save for analysis if optimizing).
10.Add 500 μL quenching buffer to beads. Vortex for 20 sec. Separate magnetically and remove supernatant.
11.Add 500 μL quenching buffer to beads. Incubate at RT for 30–60 min. Separate magnetically and remove supernatant.
12.Add 500 μL quenching buffer to beads. Vortex vigorously for 20 sec. Separate magnetically and remove supernatant. Repeat this wash twice more.
13.Remove tube from magnetic stand. Add 100 μL storage buffer. Vortex to mix and store beads at 2–8°C.
Appendix: Immobilization of Small Molecule Compounds Containing Primary Amines onto Carboxyl Magnetic Beads in Organic Phase
For screening purposes, it is essential to first optimize the amount of ligand immobilized on the beads. The immobilized ligand density can be varied by altering ligand concentration. This protocol demonstrates a method for immobilizing ligand concentrations in four steps (0 mM, 0.1 mM, 0.3 mM, and 1 mM) onto COOH-functionalized magnetic beads.
1. Materials
1.1 Beads & Ligand
・ PuriMag™ G-COOH Carboxyl Beads: 10 mg (Functional group density: Approx. 200 nmol/mg)
・ Ligand: ~2 mg
1.2 Reagents
・ N,N’-Dimethylformamide (DMF): 18 mL
・ N-Hydroxysuccinimide (NHS), M.W. 115.09: 0.1 g
・ 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC・HCl), M.W. 191.70: 100 mg
・ Aminoethanol, M.W. 61.08: 200 μL
・ Triethylamine, M.W. 101.19
・ Methanol (MeOH): 4 mL
1.3 Equipment
Centrifuge, Vortex Mixer, Rotating Mixer, Ultrasonic Disperser, Magnetic Stand
2. Method
2.1 Mechanism

2.2 Procedure
2.2.1 Active Esterification
1.Prepare 500 μL of 1M NHS solution by dissolving NHS in DMF.
2.Transfer carboxyl beads into a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube. Repeat for another tube (total 10 mg beads).
3.Perform magnetic separation at RT. Discard supernatant.
4.Add 500 μL DMF, disperse beads.
5.Perform magnetic separation at RT. Discard supernatant.
6.Repeat steps 4-5 twice more (total 3 washes).
7.During washing, add 38.4 mg (200 μmol) EDC・HCl to a new 1.5 mL tube.
8.After DMF washes, add 800 μL DMF to beads and disperse.
9.Add 200 μL prepared 1M NHS solution, mix well.
10.Transfer entire volume from step 9 into the tube from step 7. Mix well.
COOH beads (mg)
5
DMF (μl)
800
1M succinimide (μl)
200
EDC.HCl (mg)
38.4
Total (μl)
1000
11.React at RT for 2 h with vortex mixing.
12.Perform magnetic separation at RT. Discard supernatant.
13.Add 500 μL DMF, disperse beads.
14Perform magnetic separation at RT. Discard supernatant.
15.Repeat steps 13-14 four more times (total 5 washes).
16.Disperse beads in 100 μL DMF each (NHS-activated bead concentration: 2.5 mg/50 μL).
2.2.2 Ligand Immobilization
1.Prepare 1 mL of 1 mM ligand solution by dissolving ligand in DMF.
2.Prepare 3 mL of 1M aminoethanol solution in DMF.
3.Aliquot 2.5 mg (50 μL) NHS-activated beads into four microtubes. Perform magnetic separation at RT. Discard supernatant.
4.Add 200 μL DMF to each tube, disperse beads. Perform magnetic separation at RT. Discard supernatant.
5.Add DMF and prepared ligand solution. Disperse beads via ultrasonication.
Concentration (mM)
0
0.1
0.3
1
NHS beads (mg)
2.5
2.5
2.5
2.5
DMF (μl)
500
450
350
0
1mM ligand (μl)
0
50
150
500
Total (μl)
500
500
500
500
*Note 1: To prevent localized high concentration, add ligand solution after DMF has been added to beads.*
*Note 2: For hydrochloride salt ligands, add two molar equivalents of triethylamine. Prepare 4 mM triethylamine and 2 mM* *ligand solutions, then mix equal volumes.*
6.React at RT for 70 min with vortex mixing.
7.Perform magnetic separation at RT. Transfer supernatant to new tube (Supernatant A).
8.Add 500 μL aminoethanol solution to remaining beads. Disperse via ultrasonication.
9.React at RT for 2 h with vortex mixing (blocks unreacted carboxyl groups).
10.Perform magnetic separation at RT. Transfer supernatant to new tube (Supernatant B).
11.Add 500 μL 50% MeOH, disperse beads via ultrasonication.
12.Perform magnetic separation at RT. Discard supernatant.
13.Repeat steps 11-12 twice more (total 3 washes).
14.Disperse beads in 100 μL 50% MeOH and store at 4°C (ligand-immobilized bead concentration: 0.5 mg/20 μL).